Plastic welding can be used in the creation of very complex parts. Often plastic welding is used when replacing metal parts with injection moulding technology to allow the production of complex structures which otherwise would not be feasible.
Why choosing plastic welding?
If you have to create a tight container.
If you want to join two parts by a high mechanical resistance
If you want to cover with a functional part with a design part
If you want to insert a metal part into the plastic
You have several technologies to weld plastic. These have to be selected on the basis of the desired final result as every technology has its own features. Techpol masters all state of the art processes to weld plastic parts:
Vibration Welding
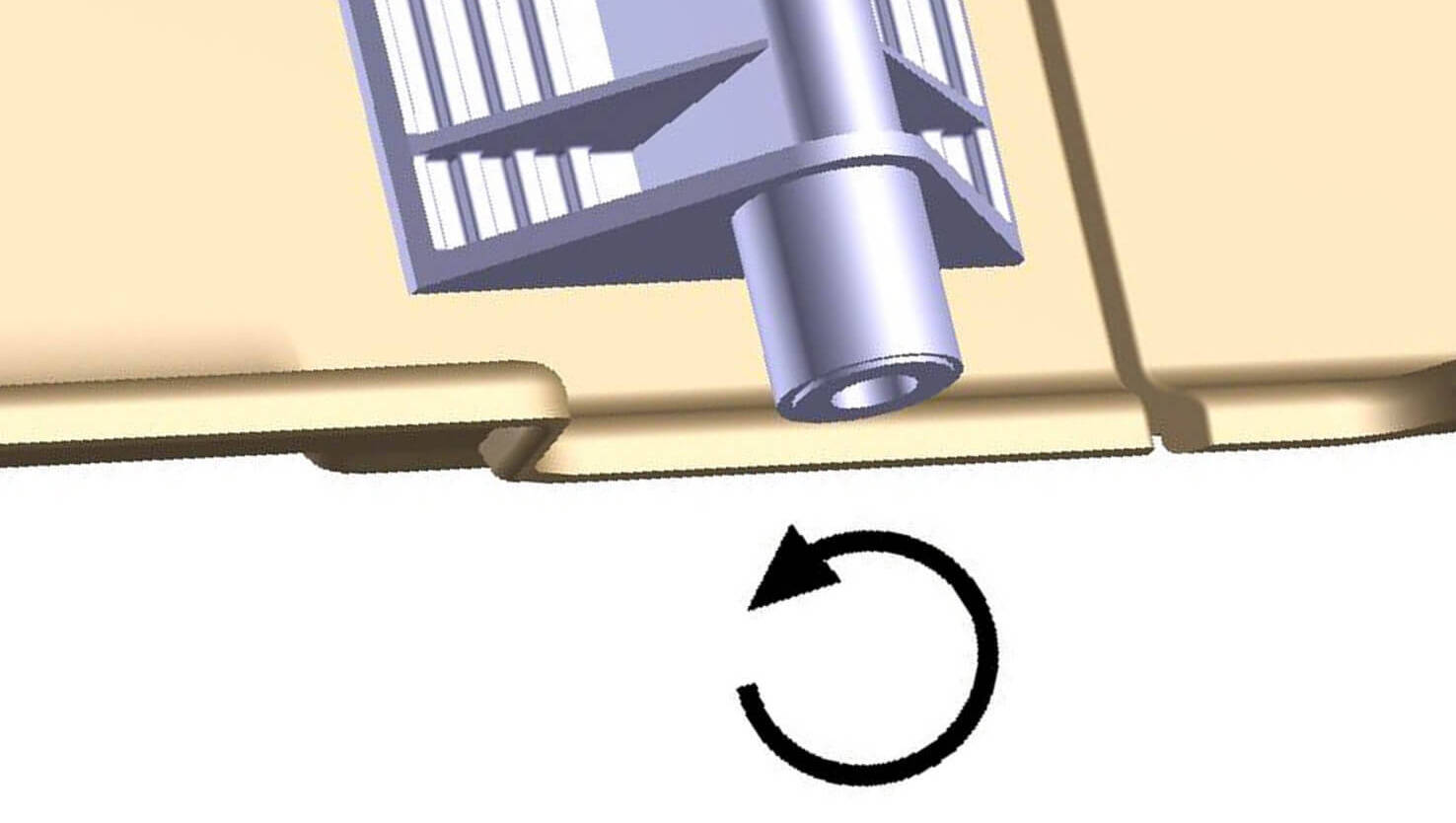
- Vibration welding is one of the most commonly used technology.
- Depth, amplitude, pressure and time can be monitored
- Flexible design of the part
- Great mechanical strength
- Suits ideally parts for high pressure applications and subject to fatigue
Ultrasonic welding
- Fast process time (approx. 1/2 second)
- Specially indicated to weld metal inserts and design cover on structural parts
- Minimal space requirement
- A vibration axis is not required
- Substitutes heat insertion
Infrared Welding

- IR welding is particularly helpful when high cleanliness level is requested
- No internal debrides (dust, burrs …)
- Welding is performed at ideal temperature
- Mechanical strength comparable to vibration welding
- Stable process, controlled and guaranteed by software application
Orbital vibration welding

- It is the same technology as vibration welding
- The movement is orbital or elliptical
- Specially indicated to weld round parts with one flat welding plane
- Limited up to 100/150mm diameter
Hot Plate

- Hot plate welding is very similar to Infrared technology and was one of the first solution used to weld plastic parts.
- Nowadays it is used only in some particular cases.
- During this kind of welding a plate/mirror is heated up until it reaches the temperature necessary to melt the materials to weld, which are in contact with the plate.
Our Engineers can check if it is possible to weld your component and make the necessary fixture with short lead-times.
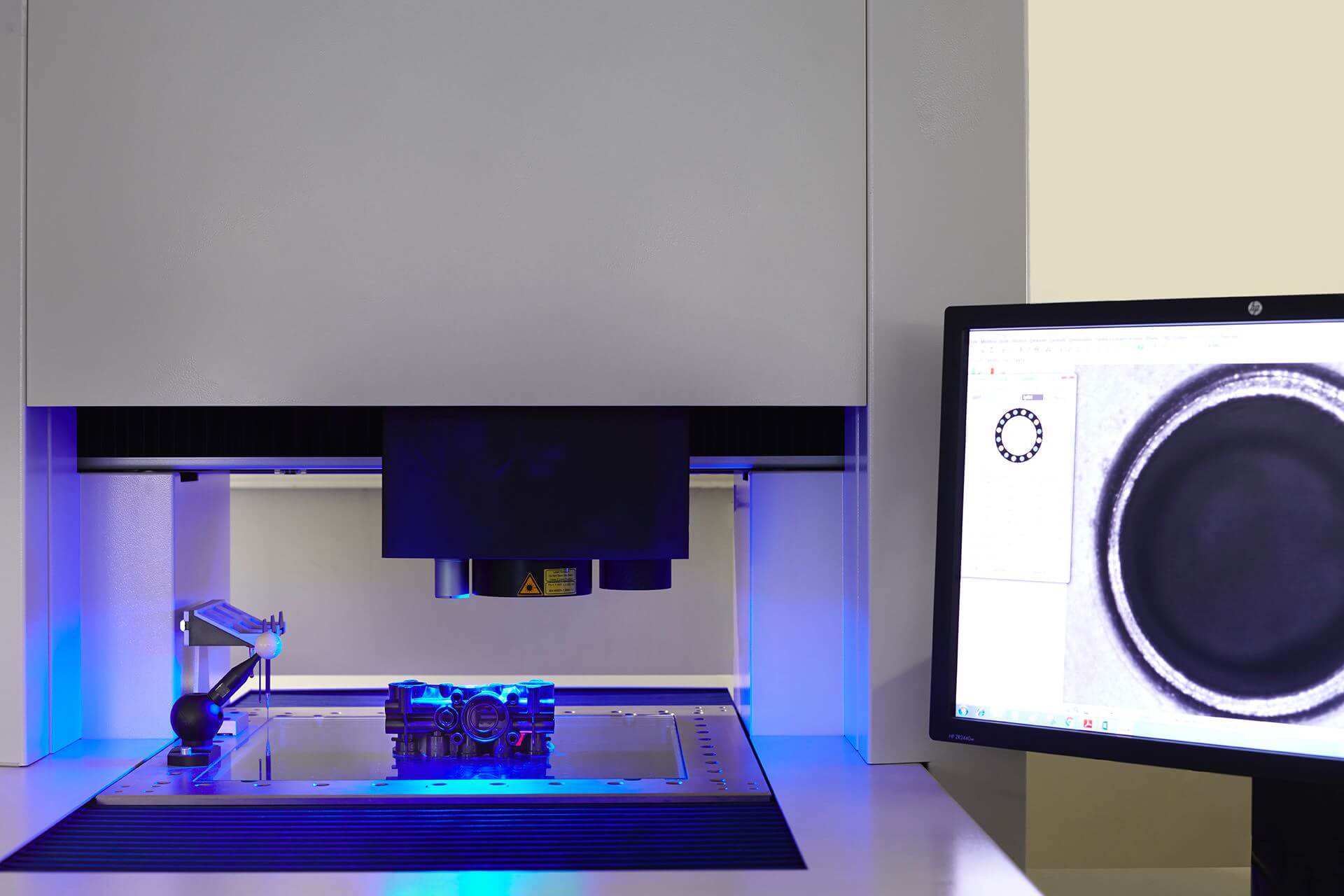
Our testing lab has all necessary equipment to test welded parts in order to assure that the product complies with technical requests.

How do we make it?







Welding process
What is needed for welding?
A welding machine of the chosen technology! Then in relation to the part which has to be welded special welding masks need to be produced.
Design of the welding profile
Independently from the chosen welding type the design of welding profile is crucial for an efficient welding. Every technology has its own peculiarities which need to be evaluated accurately.
In ultrasonic welding – as an example – the energy conveyor (the edge which will be finally melted) shall always have a sharp profile. The reason for this is that melting should start from the smaller point.
Similarly the edge on the physical mould should never be done by milling but only by etching, as with milling you could have a radius on the edge itself.
In the fiction welding on the contrary the joint should be flat and have enough room to move during friction thus allowing it to melt and join with the counterpart.
The design of all welding joints foresees containment barriers.
The reason for this design is:
- containment of melded material, which during welding can be generated in the form of burrs.
- An improved welding result as melted material meets the containment chamber and joints with the walls in this area.
Then we proceed to the final test: the software programmer and the mechanical designer carry out the first test in the workshop. When the machine is compliant it is taken to the department.
How do you ensure that the welding of the two parts was properly performed?
There are 4 typical tests for this purpose:
- Sectioning of the joint and visual test
- Traction test on the joint
- Burst test
- Leakage test
The last two tests are indicated in case you have a product with tightness requirements like for example a tank.
These tests can guarantee that the welding process was well executed and that there are no areas where the joint is just “squeezed” and not welded.
How do you ensure that the welding of the two parts was properly performed?
There are 4 typical tests for this purpose:
- Sectioning of the joint and visual test
- Traction test on the joint
- Burst test
- Leakage test
The last two tests are indicated in case you have a product with tightness requirements like for example a tank.
These tests can guarantee that the welding process was well executed and that there are no areas where the joint is just “squeezed” and not welded.
Do you want to know if your product can be welded?
Ask our advice. We will be happy to help you.
